
[ad_1]

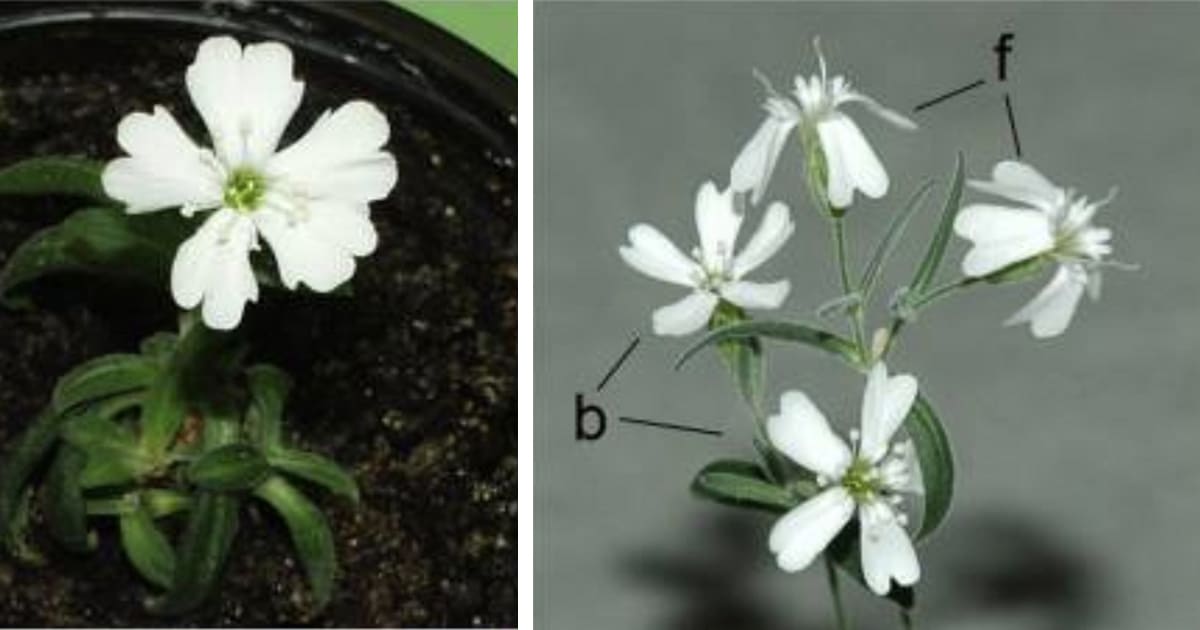
Flowering crops of Silene stenophylla. (Photo: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci United states 2012, Figure 3)
Numerous prehistoric secrets and techniques lie in the permafrost of the world’s arctic areas. Regardless of whether its a effectively-preserved mammoth or historic crops, scientists can master a ton from these organic discoveries. In 2012, a Russian staff regenerated a collection of fertile, flowering Silene stenophylla plants from 32,000-calendar year-previous seed pods. This impressive accomplishment was in depth in a paper in the Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences—an accomplishment which foreshadows other developments that could emerge from the permafrost.
The discovery of the prehistoric seed pods was element of the larger sized excavation of historical ground squirrel hibernation burrows in ice deposits in Siberia. The squirrels’ food stuff supplies experienced been trapped and preserved in the burrows, delivering a prosperity of biological proof. The fruit of the Silene stenophylla exclusively date to about 32,000 a long time in the past in the Pleistocene epoch. They introduced a obstacle for the researchers at the Russian Academy of Researchers. Earlier, the oldest regenerated plant was a Judean day palm dating to about 2,000 years ago.
The Russian crew to start with tried using to use experienced seeds from the fruit pods. On the other hand, these seeds could not generate a plant. The staff then tried using placental tissue from immature seeds. Applying cloning technology, 36 plants were being bred from the ancient material. Although they seemed like the modern Silene stenophylla which even now grows in the region, at the time the plants flowered, the petals ended up spaced further aside than in the modern day edition. Curiously, the ancient plants made seeds which generated new plants 100% of the time—a better rate than the modern-day wide range.
These 32,000-12 months-previous crops may be the critical to unlocking further more insider secrets of the permafrost.
Scientists in Russia resurrected a 32,000-calendar year-aged plant from the Siberian permafrost.

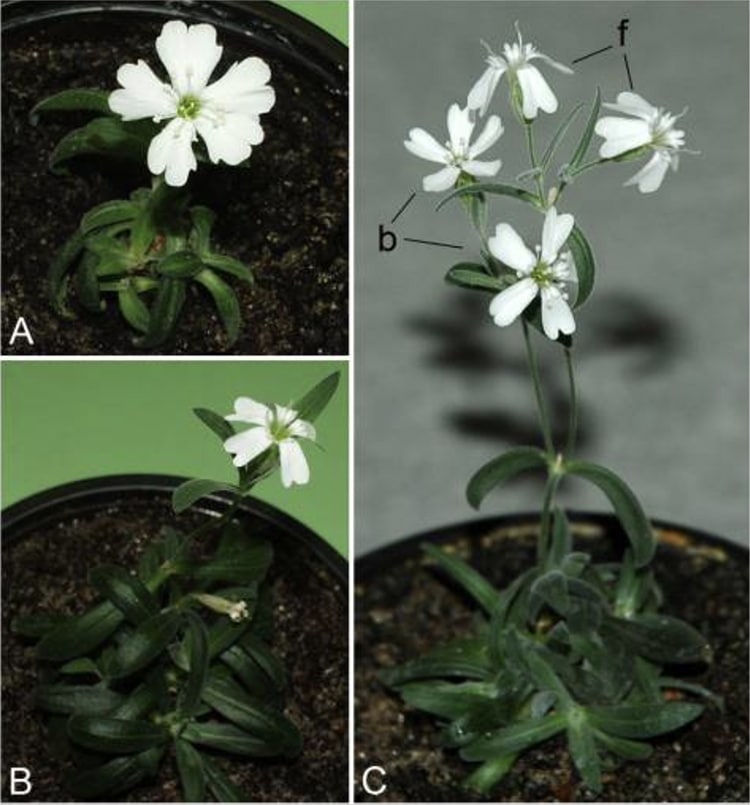
The Silene stenophylla plant fruiting. (Picture: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci Usa 2012, Figure 2)
Using cloning technological innovation and the placental tissue of immature seeds, the team raised 36 plants.
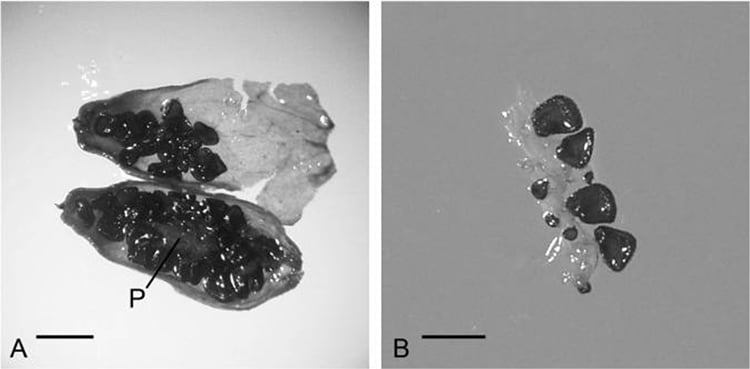
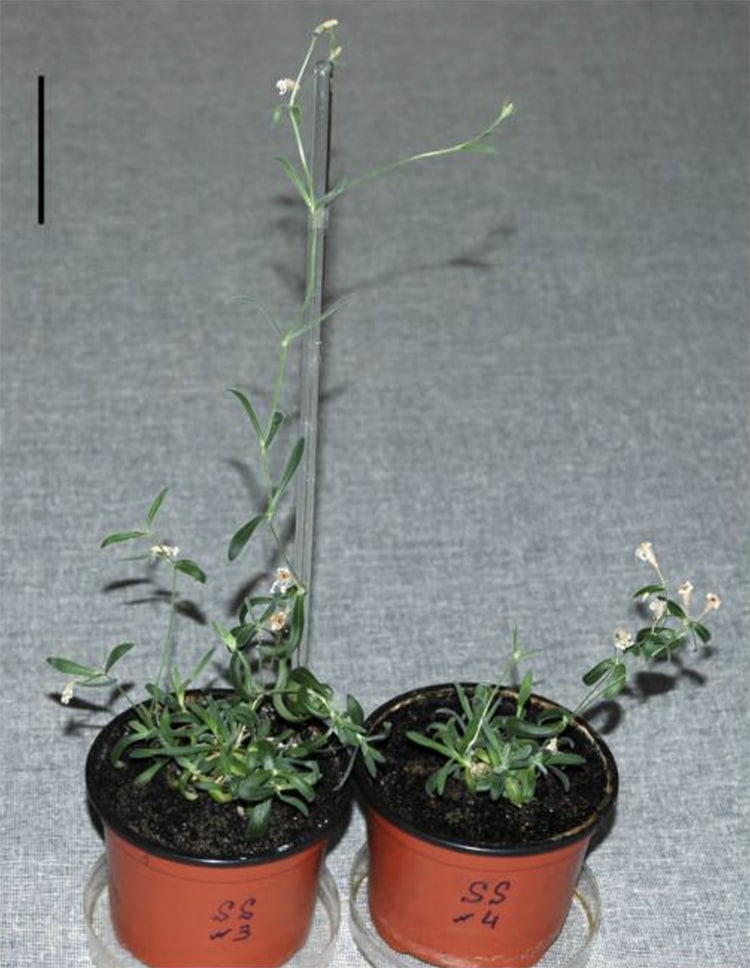
The immature fruit of Silene stenophylla which was found in the permafrost. (Picture: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci United states of america 2012, Figure 4)
The ancient plants ended up similar to the fashionable selection, with a bit more substantial and extensively-spaced petals.
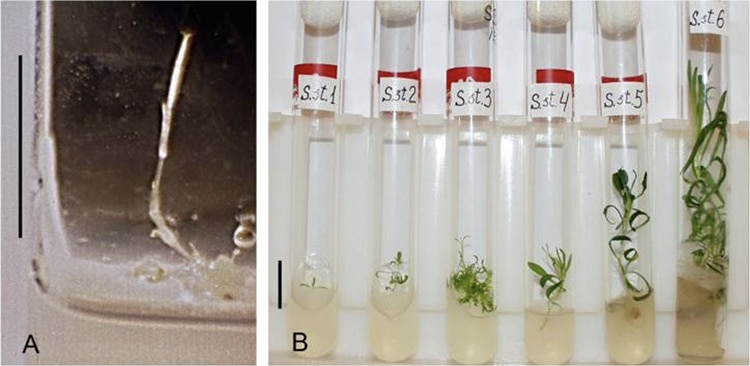
Cloning the Silene stenophylla from the uncovered fruit placenta cells. (Picture: S. Yashina et al, Proc Natl Acad Sci Usa 2012, Determine 5)
h/t: [Earthly Mission]
Associated Articles or blog posts:
Weather Transform Brings Prehistoric Plant From 60 Million Yrs In the past Again to Daily life
15,000-12 months-Outdated Bison Sculptures Are Flawlessly Preserved in a French Cave
World’s Oldest DNA Is Found in a 1.2-Million-Calendar year-Previous Mammoth
Discovery of a 9,000 Calendar year-Old Burial of a Woman Hunter Challenges Prehistoric Gender Roles
[ad_2]
Source connection







Leave a Reply