
[ad_1]

Image: VITSTUDIO/Depositphotos
Humanity is a work in progress, and sequencing the human genome has been way too. In 1990, the Human Genome Project started working to decode the elementary setting up blocks of humanity: our DNA, gathered into 23 chromosomes inside what is called a genome. By 2003, the undertaking experienced sequenced 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA. This phenomenally effective task inevitably documented 92% of the genome. Even so, it would just take virtually 20 years to decode the closing 8 %. As announced in Science, a group of researchers has at very last sequenced a whole human genome.
The previously mapped portion of the genome contained the euchromatin locations of the genome. These parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins are extra loosely packed, generating them less complicated to decode. They also enjoy basic roles in directing mobile actions. The heterochromatin regions—by contrast—were recognized as the dark issue of DNA. These dense packets of DNA material include many repeating sequences. They have lengthy been difficult to decode.
Picking up the quest the place the Human Genome Venture and subsequent experts still left off, the Telomere to Telomere (T2T) consortium developed a brain rely on of about 100 scientists. With equipment technology and handbook approaches, the researchers started to attack the dim matter portions of the genome. Their effects are at last past the peer-critique approach as the initially fully-mapped human genome.
The results will present a peek into a beforehand unknown genetic mine. The facts contained inside is likely to be helpful for scientists of inherited disorders, amid other health and fitness subject areas that place to the future of person overall health info.
The final lacking eight per cent of the human genome has been mapped to full the decades-very long undertaking of decoding humanity.
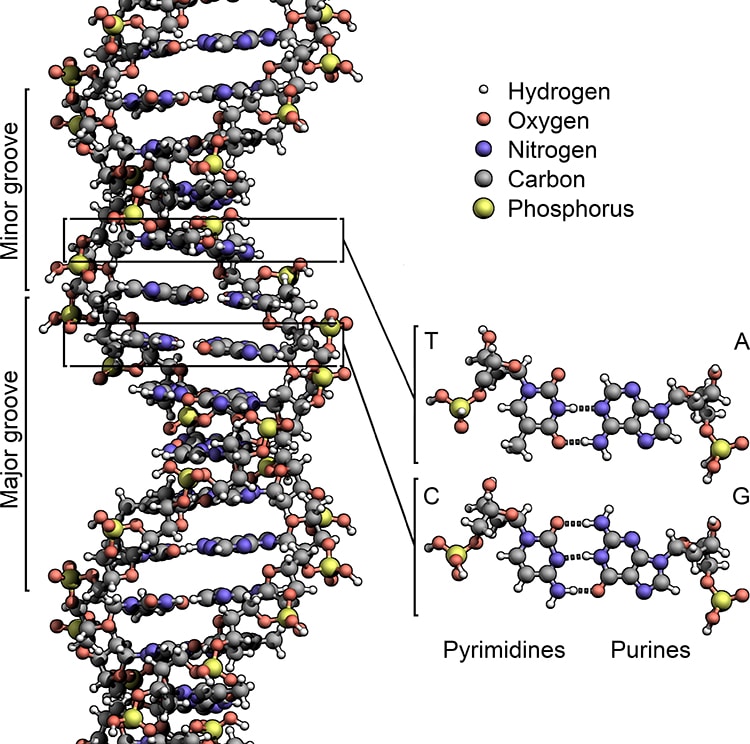

DNA structure demonstrating the iconic double helix. (Picture: Zephyris by using Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.)
h/t: [Gizmodo]
Connected Content articles:
DNA Scientists Learn 14 Dwelling Relations of Leonard da Vinci
New Proof of Earliest European People Learned in French Cave
Scientists Use DNA to Reconstruct the Faces of A few Ancient Egyptian Mummies
World’s Oldest DNA Is Learned in a 1.2-Million-Yr-Outdated Mammoth
[ad_2]
Supply link






Leave a Reply