[ad_1]
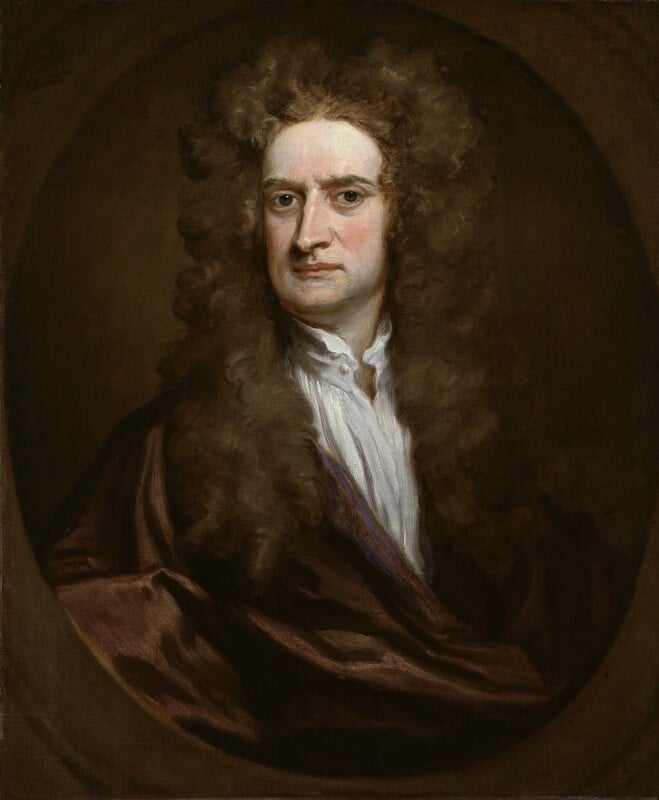

“Sir Isaac Newton,” by Sir Godfrey Kneller, 1702. (Photo: © Countrywide Portrait Gallery, London, CC BY-NC-ND 3.)
Isaac Newton is regarded for his get the job done on gravity and calculus, amid his several accomplishments. The discoveries and self-advertising initiatives of one of history’s most fantastic adult males stack up to a fascinating lifetime. Newton would implement his abilities in a lot of parts. Light, new music, the Bible—few subject areas have been beyond his curiosity and capabilities. Just what were being those myriad pursuits?
Go through on to discover Isaac Newton‘s monumental contributions.
Early Everyday living of Isaac Newton
Trinity Higher education, Cambridge, where by young Newton studied. (Picture: Wikimedia Commons, Public domain)
Isaac Newton was born in December of 1642 in Lincolnshire, England. At the time, England was briskly devolving into the English Civil War which would result in a time period of interregnum (no king) before the Restoration of King Charles II in 1660. Interregnum rule was deeply Puritan and steeped in religious philosophy. By all accounts, Newton experienced a difficult loved ones existence and was generally disappointed. He confirmed an early expertise for math, and in 1661 entered Trinity Faculty, Cambridge. It was at Cambridge that Newton researched, taught, and commenced considering the workings of the universe.
Newton’s Paradigm-Shifting Achievements
Newtonian Physics
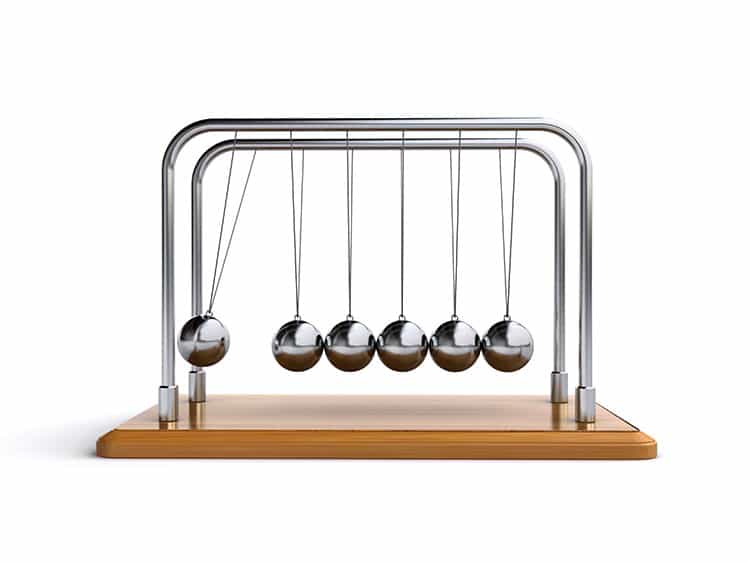

Newton’s Cradle, which demonstrates concepts of Newtonian Physics. (Image: Stock Shots from DSLAVEN/Shutterstock)
Isaac Newton is maybe best known for his “discovery” of gravity. Though gravity constantly existed, legend states that Newton had an epiphany when strike by an apple slipping from a tree over. Though he was the very first to postulate a idea of universal gravitation, his contributions to our knowledge of the bodily entire world had been, in reality, substantially broader. Newton’s popular perform entitled Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica (Mathematical Concepts of Natural Philosophy, 1687) laid out the associations that every higher university scholar learns nowadays in their introduction to what is recognized as classical mechanics.

Isaac Newton’s “Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica” annotated in his gained hand for the 2nd version. (Image: Billthom by means of Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.)
The Principia describes the legislation of universal gravitation—Newton’s discovery that all objects in the universe exert a gravitational pull on just about every other in amounts that can be calculated dependent on their respective masses and length aside. The 3-volume ebook also released a few rules of motion. The very first is that an object in motion will remain in motion at the similar velocity except if acted on by an outside the house power. The second describes an critical equation: force is equivalent to mass periods acceleration. Finally, the third is a popular declaring of bodily truth: for each individual motion, there is an equal and reverse reaction.
Optics
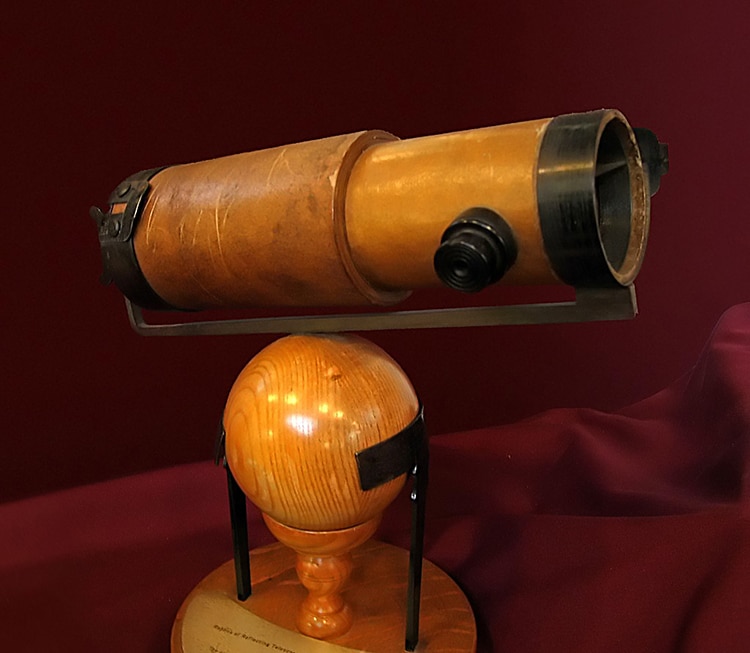

A reproduction of Newton’s 2nd reflecting telescope structure. (Picture: Andrew Dunn through Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 2.)
Newton manufactured significant developments in the field of optics. Although a professor at Cambridge, he analyzed gentle refracted through a prism, which—like on the Pink Floyd album cover—splits the white mild into its component hues. He realized that the spectrum of colors is intrinsic to distinct rays of mild. The light-weight retains its colour no matter wherever it shines. The beams can also be introduced again into a single beam of white gentle making use of one more prism. Newton also considered that light-weight was made up of particles—an view which his popular fellow scientist Robert Hooke vehemently turned down in favor of a wave principle.
At the time, early telescopes employed refracting lenses to magnify a field of view. Newton was worried about chromatic aberrations owing to the prisms refracting of gentle. As a consequence, he set about developing a reflecting telescope that used mirrors to enlarge an graphic. He crafted his very first telescope in 1668. In 1671, he showed his newest model to the Royal Society of London, of which he shortly became a member. It was a hit, and Newtonian telescopes are nevertheless created in versions today.
Calculus

Newton’s “The strategy of fluxions and infinite sequence, with its software to the geometry of curve-traces,” prepared in 1671 but revealed posthumously in 1736. (Picture: Beinecke Library, Yale College, General public area)
Who has heard of Gottfried Leibniz? The remedy is considerably fewer folks than those who know Newton’s title. This is mainly due to Newton’s fame in other parts. Even so, the other founder of calculus’ title has absent down in heritage for his academic tensions with the English physicist. Calculus is primarily the research of curves by pinpointing the location below them or their slopes. The German Leibniz published his work on curves prior to Newton. Nonetheless, Newton’s earlier notes demonstrated he arrived up with his very own solutions through his reports of planetary movement.
So who invented calculus? Very well according to Newton, he did. From his effective posture in the Royal Culture, Newton built the “decision” of an “impartial” committee in his favor. Nonetheless, the two are normally recognized these days. Relatively than cheating off one a further, they probable made their developments in parallel, as oft comes about in STEM.
Other Pursuits: Alchemy, Faith, & Music
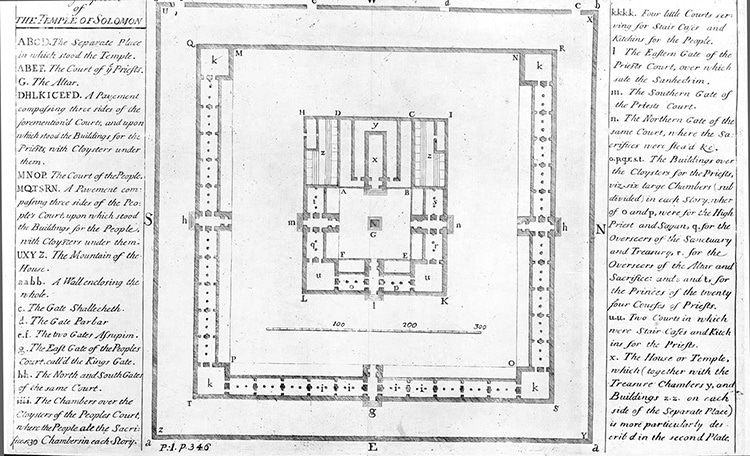
Isaac Newton’s rendering of the Temple of Solomon, from his “The chronology of historical kingdoms amended,” 1728. This edition is housed at the Beinecke Uncommon Ebook and Manuscript Library, Yale University. (Photo: Wikimedia Commons, Community domain)
In the 17th century, science was a relatively open-ended industry. Factors this kind of as horoscopes and the search for the Philosopher’s Stone were not scorned by even the most established experts. Newton had sufficient fascination in alchemy, which at the time was intently entwined with the subject that developed into modern chemistry. He experimented with metals and concoctions, at a single issue burning down his lab with most of his notes.
Continuing a classical custom, Newton observed audio as owning scientific connections to character. Newton included orange and indigo to the five current colours of the rainbow as his review of light seemed deeply tied to musical scales. Even religion was a field upon which Newton sought to make his mark. Newton studied and sketched the Temple of Solomon based on his readings of scripture and suggestions of sacred geometry. He also wrote on the ancient civilizations of the Bible in a operate entitled The Chronology of Historic Kingdoms Amended, posted posthumously in 1728.
The Afterlife of a Genius

Newton’s apple tree at Porter’s Lodge, Cambridge. (Photo: Image: Inventory Photos from EMILY GOODWIN/Shutterstock)
Newton accomplished unusual fame in his life time. A polymath, he revolutionized disparate fields. Passing away at 84 in 1727, he remaining at the rear of a Royal Culture shaped by his management, bigger-than-life mythology, and the guidelines of the universe which are however taught nowadays.

The Wren Library at Trinity School, Cambridge, in which lots of of Newton’s works are housed. (Photograph: Andrew Dunn by way of Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 2.)
Though challenging by Einstein’s Normal Relativity and other much more latest developments, Newtonian physics describes so considerably of what we see today—pool balls darting across tables, autos accelerating, and divers leaping off platforms. For Newton, learning the world was a industry in and of alone.
Relevant Content articles:
29 Famous Experts Came Together in the “Most Clever Photo” At any time Taken
Amazing Restored Pics of Earth Taken by Apollo Astronauts
Who Was Marie Curie? Discover Additional About This Groundbreaking Nobel Prize Winner
Satisfy the Harvard Desktops, the Undervalued Girls Who Mapped 400,000 Stars
[ad_2]
Supply url



